At this point it is also important to highlight the significance of pre-surgery preparation. The better we prepare; less is the chance of having complications. Preparation for bariatric surgery includes- pre-surgery diet, pre-operative supplementation of nutritional deficiencies, medical optimization of associated diseases, incentive spirometry and so on.
Before we get onto the discussion on individual complications, let us evaluate the complication rate of bariatric surgery as compared to other major surgeries. This will give us some more perspective.
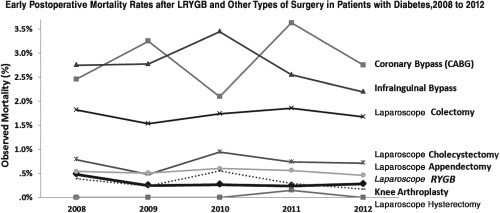
Fig:1- Early post-surgery mortality rate after Roux-en y gastric bypass as compared to other surgeries in patients with diabetes [1]
As is evident from the graph, complications and mortality after bariatric surgery is comparable to other surgeries like a laparoscopic hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), appendicectomy, cholecystectomy (removal of the gall bladder) or a total knee arthroplasty. Bariatric surgery is also less risky as compared to a coronary bypass (CABG) or a colectomy.
In this blog we will discuss the early and late complications after the three most commonly performed bariatric surgeries in India-
- Complications after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG)
- Complications after laparoscopic Roux-en y gastric bypass (LRYGB)
- Complications after laparoscopic one anastomosis gastric bypass or mini gastric bypass (MGB/OAGB)
Early complications are almost similar in all bariatric operations and are listed as under:
- Anaesthesia related complications
- Venous thrombo-embolism (Deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism)- Patients suffering from severe obesity are prone to developing a blood clot in their leg veins. At times this can travel up to their heart or lungs. This is one of the most catastrophic complications and can be fatal. We take all precautions in terms of blood thinner medications, compression stockings and pumps and early mobilization to prevent this.
- Intra-operative injuries to other organs– Rarely, other organs like liver, spleen, intestine mesenteric fat or blood vessels may get injured during surgery. If detected early, these can be tackled effectively.
- Haemorrhage or bleeding– This can occur due to injury to a blood vessel or sometimes bleeding may also happen from staple line or the anastomotic sites.
- Leaks– Leaks can happen from any staple lines or any of the anastomosis. This leads to leakage of the enteral contents into the abdominal cavity. This can lead to localized infection or sometimes widespread septicaemia.
- Wound infection– The rates of wound infections have come down drastically since the advent of laparoscopy. However, sometimes the wound may still get infected
Late complications
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD)– LSG is considered to be a refluxogenic operation and some patients may develop varying degree of acid reflux after this surgery in the long term. Patients are usually treated with medications and if they do not get relief, a revision surgery in the form of conversion to a laparoscopic Roux-en y gastric bypass may be needed.
- Stricture or kinking of the sleeve– This can happen sometimes and lead to difficulty in swallowing or vomiting in severe cases. It usually settles down with endoscopic dilatation and if that fails the sleeve may need to be converted to a Roux-en y gastric bypass.
- Weight regain– As time passes by, sleeve of stomach does tend to expand and thus the ability to consume food increases over time. Hence, to maintain the weight loss it is important to have a healthy diet and exercise regularly. If the weight regain cannot be controlled with diet and lifestyle modification, then weight loss medications are prescribed. If the response to that is not satisfactory, revision surgery may be required.
- Nutritional deficiency– Nutritional supplements are needed even after sleeve gastrectomy. Iron and multi-vitamin deficiency is known and needs to be monitored. Inability to take supplements regularly can lead to nutritional deficiencies that can have a wide variety of manifestations.
Laparoscopic Roux-en y gastric bypass
- Marginal ulcers– These can occur at the anastomotic site where the stomach is joined with the small intestine. These are more common in patients who are on pain-killer medications, steroids or those who smoke regularly. It is important to do a yearly UGI endoscopy to detect these and these are treated with antacid medications. In severe cases, a resection of the ulcer site with revision of the anastomosis may be needed.
- Internal hernia– In case of a Roux-en y gastric bypass, the intestines are realigned and artificial spaces are created. Small intestine can herniate through these spaces and lead to obstruction. A re-laparoscopy is usually required to treat internal hernia.
- Nutritional deficiency– It is important to take nutritional supplements like iron, multi-vitamin, calcium and protein regularly. Inability to take supplements regularly can lead to nutritional deficiencies that can have a wide variety of manifestations.
- Diarrhoea– Some patients can develop diarrhoea after Roux-en y gastric bypass. It is usually self-limiting but at times medications may be needed.
- Dumping syndrome– Sudden influx of carbohydrate rich food into the small intestines leads to dumping syndrome. This may manifest with low sugars, sweating, palpitations, diarrhoea, crampy pain in the abdomen and so on. Both early and late dumping are seen after Roux-en y gastric bypass. This can be treated effectively with dietary changes and medications.
- Weight regain- Obesity is a chronic and progressive disease and weight regain can happen after any bariatric procedure. While anatomical causes like dilatation of the pouch or the anastomosis may play a part, the significance of healthy diet and a regular exercise regime is paramount. Weight loss medications are used off and on to tackle weight regain and in severe cases revision surgery may be needed.
Laparoscopic one anastomosis gastric bypass or mini gastric bypass
- Marginal ulcers– These can occur at the anastomotic site where the stomach is joined with the small intestine. These are more common in patients who are on pain-killer medications, steroids or those who smoke regularly. It is important to do a yearly UGI endoscopy to detect these and these are treated with antacid medications. In severe cases, a resection of the ulcer site with revision of the anastomosis may be needed.
- Biliary reflux– As one anastomosis gastric bypass or mini gastric bypass is an operation with a loop anastomosis, bile from the afferent loop flows through the anastomosis into the efferent loop. It can reflux into the stomach pouch and sometimes in severe cases it can reflux into the food-pipe as well.
- Nutritional deficiency– It is important to take nutritional supplements like iron, multi-vitamin, calcium and protein regularly. Inability to take supplements regularly can lead to nutritional deficiencies that can have a wide variety of manifestations. Protein deficiency can be particularly troublesome in Indian patients as the non-vegetarian intake is much lower. It is extremely important to take protein supplement regularly after one anastomosis gastric bypass or mini gastric bypass.
- Diarrhoea– Some patients can develop diarrhoea after one anastomosis gastric bypass or mini gastric bypass. It is usually self-limiting but at times it can be severe and can affect the quality of life poorly.
- Dumping syndrome– Sudden influx of carbohydrate rich food into the small intestines leads to dumping syndrome. This may manifest with low sugars, sweating, palpitations, diarrhoea, crampy pain in the abdomen and so on. Both early and late dumping are seen after one anastomosis gastric bypass or mini gastric bypass. This can be treated effectively with dietary changes and medications.
- Weight regain- Obesity is a chronic and progressive disease and weight regain can happen after any bariatric procedure. While anatomical causes like dilatation of the pouch or the anastomosis may play a part, the significance of healthy diet and a regular exercise regime is paramount. Weight loss medications are used off and on to tackle weight regain and in severe cases revision surgery may be needed.
These are the common complications after bariatric procedures. If you notice anything out of the ordinary, you must immediately get in touch with us. Any complication when detected early can be managed better. Not all patients develop complications. However, bariatric surgery is not a one-time event. It is a lifelong commitment by the patient and the bariatric team. Patients who are regular with their follow up and nutritional supplementation have better results in every way.
Thank you.
Dr. Aparna Govil Bhasker
About Dr. Aparna Govil Bhasker

Read more about Dr. Aparna Govil Bhasker- https://www.bestbariatricsurgeon.org/dr-aparna-govil-bhasker/
Please write in to info@bestbariatricsurgeon.org or draparnagovil@gmail.com & Call/Text/WhatsApp: +919819566618 or +919930922761
Dr. Aparna’s website is- https://www.bestbariatricsurgeon.org
You can read her lovely blogs on- http://www.aparnagovilbhasker.com
Dr. Aparna Govil Bhasker is a visiting bariatric surgery or weight loss consultant at the following hospitals:
- Saifee Hospital, Charni Road, Mumbai
- Gleneagles Global Hospital, Parel, Mumbai
- Apollo Spectra Hospital, Tardeo and Chembur, Mumbai
- Namaha Hospital Kandivali, Mumbai
- Suchak Hospital, Malad, Mumbai
- Currae Specialty Hospital, Thane
- Surya Hospital, Santacruz West, Mumbai
- Hinduja Healthcare Surgical, Khar West, Mumbai
- Apollo Hospital, CBD Belapur, Navi Mumbai
- MGM Hospital, Vashi, Navi Mumbai
Social Media:
- Facebook- https://www.facebook.com/draparnagovilbhasker/
- Linked in- https://www.linkedin.com/in/dr-aparna-govil-bhasker-82836b34/
- Twitter- https://twitter.com/aparnabhasker
- Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/draparnagovilbhasker/?hl=en
- You tube- https://www.youtube.com/user/aparnagovil/videos?view_as=subscriber