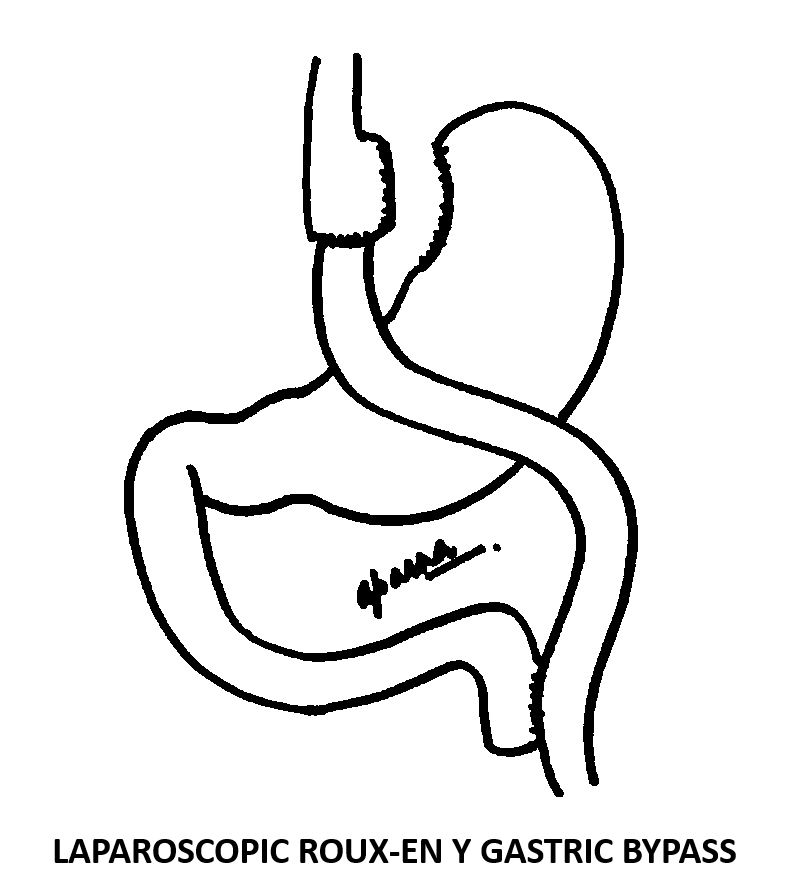
Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass is a type of weight-loss/bariatric surgery. As the name suggests it can be performed through key-hole method (laparoscopy). In this technique 4 to 5 tiny cuts of half to one cm are made on the abdomen and the whole surgery is performed through these. In another variation of a Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass a silicon band may be applied around the stomach pouch. This is known as the Banded Roux en-y gastric bypass surgery. In a Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass surgery, a small 30 to 50 cc stomach pouch is created using surgical staplers. Small intestine is divided at about 50 to 100 cm from the duodeno-jejunal junction and attached to the stomach pouch in a “y” shaped fashion. The food comes into the stomach pouch and flows directly into the small intestine. It bypasses the remaining stomach and the first part of small intestine.
Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass surgery in mumbai leads to weight loss by various mechanisms. First of all, it leads to restriction of food intake. After a Roux en-y gastric bypass, the stomach pouch can hold only 30 to 50 cc of food at one go. This reduces the amount of food that a person can have. As the stomach size is small, it also leads to feeling full sooner. The feeling of satiety sets in after eating even small quantities of food. After a Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass “hunger” sensation goes down significantly. This happens because the part of the stomach that is bypasses contains almost 80% of the hunger hormone called “ghrelin”. As the food does not come in contact with this part of the stomach, for the first year, most patients do not experience “hunger”. Hence, they are satisfied even after eating less food which is unlike being on a diet where one is constantly battling hunger and cravings. As the food also passes into the intestines faster than usual and this sets of a hormonal cascade that also aids in weight loss as well as helps in remission of type 2 diabetes. Ofcourse, there are other mechanisms like bile acid interactions and role of gut microbes. Alongwith these there are some unknown mechanisms and all of these when put together lead to weight loss after Roux en-y gastric bypass.
Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass leads to an excess weight loss of about 70 to 80% in 12 to 18 months. Patients also experience significant improvement in associated diseases like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, gout, PCOD, obstructive sleep apnoea, joint pains, liver disease etc. It also reduces the risk of venous thrombo-embolism and heart disease in the long term. Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass leads to a significant improvement in the quality of life of the patient.
In the long term the main issues observed with a laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass are possible nutritional deficiencies and some degree of weight regain. However, obesity is a chronic progressive disease and as with any weight loss procedure, regular follow up with the bariatric surgeon team is the key to success after a laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass. It is extremely important to follow a healthy lifestyle and a good exercise regime after a Laparoscopic Roux en-y gastric bypass.
Dr. Aparna Govil Bhasker is a Bariatric and Advanced Laparoscopic Surgeon.
Affiliations: Global Hospital, Parel; Apollo Hospitals, CBD Belapur, Tradeo and Chembur; Currae Hospital, Thane; Suchak hospital, Malad and Namaha Hospital, Kandivali
Mobile: +91 9819566618
Email: draparnagovil@gmail.com
Website: www.bestbariatricsurgeon.org